The term Artificial Intelligence (AI) has officially left the realm of science fiction and is now shaping your everyday life.
But what is it? Is it just complicated software? Is it a robot that thinks and feels? The definition can seem slippery because AI is less a single technology and more an entire field of computer science dedicated to giving machines human like intellectual capabilities.

This guide is your complete, beginner friendly blueprint. We’ll break down exactly what artificial intelligence is, how it works, the core concepts that power it, and the four distinct types that exist today, all without the overwhelming jargon.
By the end, you’ll not only understand AI, but you’ll be able to explain it to someone else with clarity and confidence.
Section 1: Decoding the Core Concept with the ‘AI Brain’ Analogy
Let’s start with the most simple, memorable way to understand AI: The AI Brain Analogy.
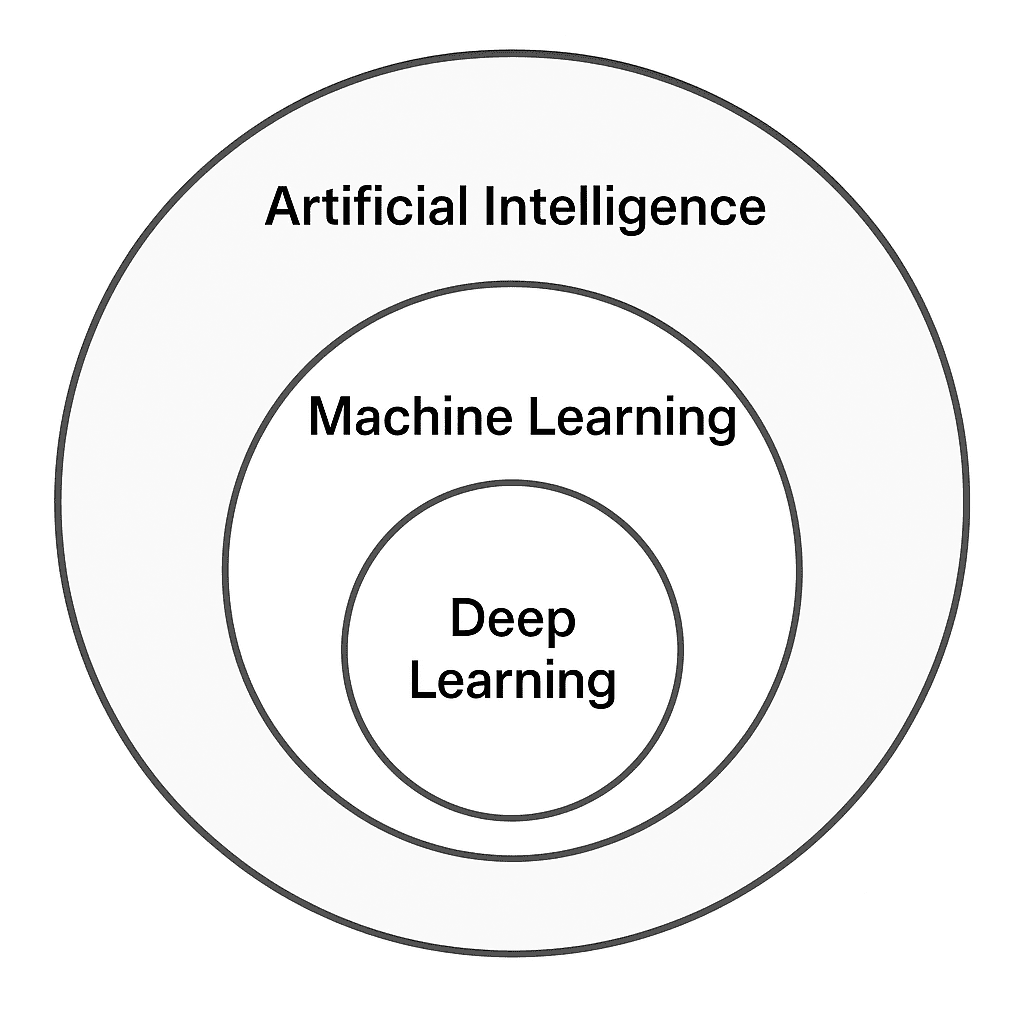
Think of the entire field of Artificial Intelligence as a machine that seeks to simulate human intelligence.
It’s the overarching goal the entire brain. To achieve this goal, it uses several critical tools, two of the most important being Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
What is AI in simple words?
In simple words, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the science of building computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
This includes things like learning, decision making, visual perception, problem solving, and understanding language.
The goal isn’t necessarily to replace the human brain, but to create tools that can process information and act intelligently, often on a scale or speed that humans can’t match.
| Component | Analogy Role | Simple Definition |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | The ultimate Goal (The Brain) | The broad field of making machines smart—able to reason, plan, and solve problems. |
| Machine Learning (ML) | The Method of Learning (The Training) | A subset of AI where systems learn from data to identify patterns and make predictions without being explicitly programmed for every possible scenario. |
| Deep Learning (DL) | The Advanced Technique (The Cortex) | A subset of ML that uses Artificial Neural Networks (layers of virtual ‘neurons’) to process complex, unstructured data like images, sound, and text. |
What is the difference between AI and machine learning?
The critical difference is that Machine Learning (ML) is a sub field of AI. AI is the destination (intelligent behavior), and ML is one of the primary vehicles we use to get there (learning from data).
- Traditional AI relied on explicit programming (e.g., “If condition X, then action Y”).
- Machine Learning learns from examples. You give it millions of pictures of cats and dogs, and it teaches itself the difference.
Without machine learning, AI would be a static, rule based program. ML gives AI the power to adapt, improve, and predict.
Section 2: The Two Fundamental Types of Artificial Intelligence
When people talk about AI, they are usually referring to its capabilities, which are categorized into two primary forms based on their scope and power.
Weak AI (Narrow AI)
Weak AI, also known as Narrow AI, is the only type of AI that currently exists.
- Scope: It is designed and trained to perform a single, specific task or a very narrow range of tasks.
- Intelligence: It simulates human intelligence but does not possess true human consciousness or awareness. It is a highly specialized tool.
- Examples: All the AI you use daily—Siri, Alexa, Google Search, Netflix recommendation engine, self driving cars, spam filters, and tools like ChatGPT.
Narrow AI may be incredibly good at its one task—often better than a human (like a chess AI)—but it cannot generalize its intelligence. A chess AI can’t suddenly start writing poetry, and a self driving car can’t perform heart surgery.
Strong AI (Artificial General Intelligence AGI)
Strong AI (or Artificial General Intelligence AGI) is the hypothetical type of AI that does not yet exist.
- Scope: It would possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply its intelligence to solve any problem, just like a human being.
- Intelligence: It would have a full range of cognitive abilities, including consciousness, self awareness, and common sense.
- Examples: Fictional AIs like Data from Star Trek or the robots from I, Robot.
AGI is the holy grail of AI research, but its creation is still theoretical and poses immense technical and philosophical challenges.
The Four Stages of AI Development: Beyond Weak and Strong
Researchers further categorize AI into four hierarchical types based on their potential complexity and ability to mimic the human mind.
1. Reactive Machines
The most basic form. They can only react to current situations, having no memory of past experiences to inform future decisions.
- Example: IBM’s Deep Blue, which defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov. It could see the current board and choose the best move, but it couldn’t learn from a past match.
2. Limited Memory AI
The bulk of current AI technology. They can look into the recent past (limited memory) to make informed decisions.
- Example: Self driving cars use sensors to observe the speed and direction of other cars around them to safely navigate. This short term data is the “limited memory.”
3. Theory of Mind AI (Theoretical)
This is the next level of hypothetical AI. It would be able to understand human emotions, beliefs, intentions, and thought processes, allowing it to socially interact effectively.
- Example: An AI therapist that genuinely understands and responds to the nuance of your emotional state.
4. Self Aware AI (Theoretical)
The final stage—the ultimate goal. This AI would possess a sense of self, consciousness, and awareness of its own state. This is Strong AI.
- Example: The fully sentient, feeling, and thinking machine often depicted in movies.
Section 3: How Does AI Work? The Foundation of Training
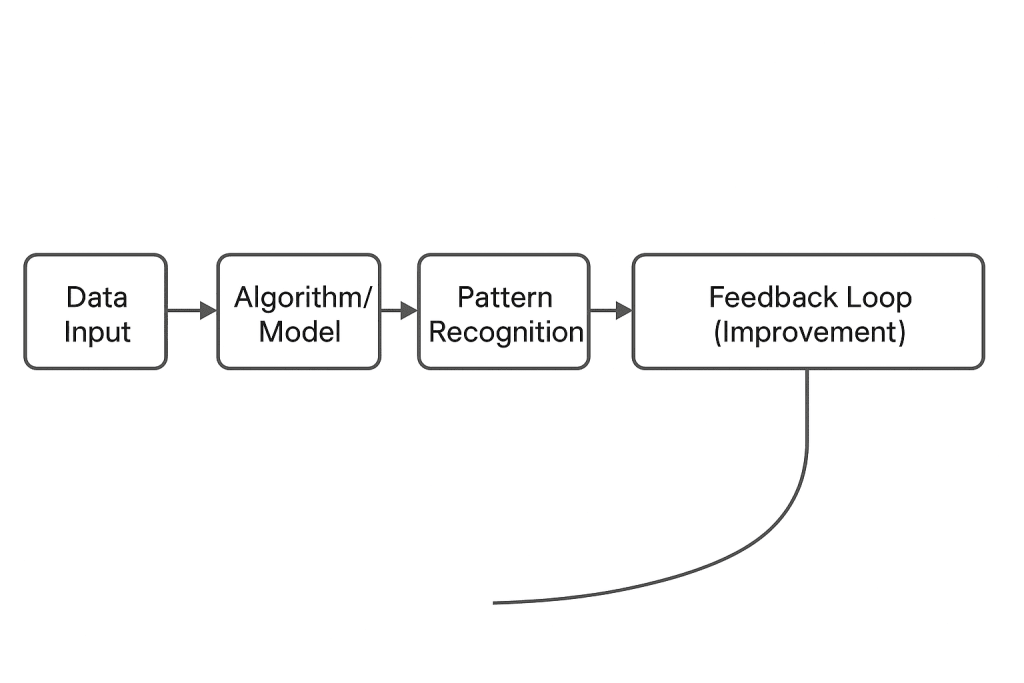
The power of modern AI, especially Machine Learning, comes from its ability to learn from data, not just follow rules. This is achieved through a core, three step process: Data, Algorithms, and Training.
How does AI work?
AI systems work by taking massive amounts of data (images, text, numbers), feeding them into algorithms (mathematical instructions), and using this combination to recognize patterns and make predictions or decisions. This process is called training.
Imagine teaching a child to recognize a cat:
- Data Ingestion: You show the AI system millions of pictures (the data) labeled “cat” or “not cat.”
- Algorithm (The Rules): The machine uses algorithms (like neural networks) to look for recurring features—pointy ears, whiskers, etc.
- Pattern Recognition & Prediction: When shown a new, unlabeled picture, the AI can recognize these features, compare them to the patterns it learned, and predict: “This is a cat.”
- Learning & Improvement: If the prediction is wrong, the algorithm adjusts its internal mathematical “weights” to be more accurate next time. It learns and improves with every new piece of data.
Core Pillars of Modern AI Technology
The practical applications of AI are built upon several specialized fields:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
The most common way to build AI today. It is the ability to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML is used for making predictions (which customer will churn?), classifications (is this email spam?), and recommendations (what show should you watch next?).
2. Deep Learning (DL)
A step beyond ML, DL uses deep Artificial Neural Networks—structures inspired by the human brain’s interconnected neurons—to handle highly complex, unstructured data.
- Application: Used for advanced tasks like translating languages or generating realistic images and video.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This gives machines the ability to read, understand, and generate human language.
- Application: Powers virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa), chatbots, text summarization tools, and machine translation (Google Translate).
4. Computer Vision
This field gives machines the ability to “see” and interpret the world through images and video.
- Application: Facial recognition, self driving car navigation, medical image analysis (detecting tumors), and quality control on assembly lines.
Section 4: The Generative AI Revolution: New Capabilities and Applications
Generative AI (GenAI) has taken the world by storm because it represents a significant leap in machine capability. It’s the AI that creates, rather than just predicts or classifies.
Generative AI is a form of Deep Learning that can create brand new content—including text, images, code, audio, and video—that has never existed before, based on the patterns it learned from its training data.
Is ChatGPT an AI?
Yes, ChatGPT is a prominent example of Narrow AI, specifically a type of generative AI.
It uses a Large Language Model (LLM), which is a massive, deep neural network trained on a huge dataset of text and code. This training enables it to understand context and generate human like, coherent, and contextually relevant text in response to a user’s prompt.
It is highly advanced, but it remains Narrow AI because its function is limited to language generation, and it is not truly conscious or self aware.
The Rise of Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs are the engine behind the current AI boom. They work by learning the complex statistical relationships between words.
When you give it a prompt, the model essentially predicts the most statistically probable sequence of words that should follow, building a coherent response one word at a time.
- Predictive AI (Old Way): Asks, “Will this email be spam?” (Classification)
- Generative AI (New Way): Asks, “Write me an email about a promotion.” (Creation)
| Generative AI Model | Output | Everyday Example |
| Large Language Models (LLMs) | Text, Code | ChatGPT, Google Gemini, GitHub Copilot |
| Diffusion Models | Images, Video | DALL E, Midjourney, Stability AI |
| Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) | Realistic Faces, Data Synthesis | Creating hyper realistic, fictional celebrity faces |
Section 5: A Brief History: From Concept to Boom Time
The idea of intelligent machines is ancient, but the formal field of AI is quite young. Understanding its history explains why the technology has only recently gone mainstream.
| Decade | Key Event | Significance |
| 1950 | Turing Test Proposed | Alan Turing asks: Can a machine pass for a human in conversation? This sets the philosophical goal for AI. |
| 1956 | Dartmouth Summer Research Project | John McCarthy coins the term “Artificial Intelligence.” The field is officially born, driven by the goal of Symbolic AI (rule based systems). |
| 1974 1980 | First AI Winter | Initial optimism fades as the limitations of Symbolic AI (Expert Systems) become apparent and funding dries up. |
| 1980s | Expert Systems Boom | A brief resurgence driven by specialized, rule based programs for business. |
| 1987 1993 | Second AI Winter | Expert systems prove too expensive and difficult to maintain. Researchers turn toward statistical, connectionist methods (Neural Networks) with limited success. |
| 1997 | Deep Blue Defeats Kasparov | IBM’s chess program beats the world champion, demonstrating the power of Narrow AI combined with massive computing power. |
| 2012 Present | Deep Learning Revolution | Cheaper, faster GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and the availability of Big Data enable the training of large, complex Deep Neural Networks. This triggers the current AI Boom. |
The key takeaway is that the AI we see today is the result of breakthroughs in computing power and data availability—not a sudden, recent invention.
Section 6: Actionable Steps for the Beginner: Navigating the AI World
Now that you know what AI is, how do you interact with it and stay current? The barrier to entry has never been lower.
What is the main goal of AI?
The main goal of AI is to create intelligent systems that can function autonomously, making decisions, solving problems, and performing tasks that typically require a human mind.
The secondary, practical goal for most companies developing AI is to increase efficiency, automate repetitive tasks, and uncover patterns in data at a scale impossible for humans.
5 Specific Ways to Engage with AI Today
- Try a Generative AI Tool:
- Action: Go to a free chatbot (like a public Large Language Model) and ask it to write you an email, summarize a difficult concept, or suggest a five day meal plan. This is the fastest way to understand its power and limitations.
- Use a Simple AI Art Generator:
- Action: Use a free AI image generator to bring a strange or abstract idea to life. This instantly illustrates the concept of Generative AI’s creativity.
- Read an AI Powered News Feed:
- Action: Observe how platforms like Netflix, Spotify, or your social media feed use AI to recommend content. Take a moment to think about what data the system used to make that specific recommendation to you.
- Explore a Free Online Course:
- Action: Many top universities (MIT, Stanford) and platforms (Coursera, edX, Google AI) offer free introductory courses on AI and Machine Learning. Look for courses like “AI for Everyone” to get a non technical overview.
- Identify Narrow AI in Your Home:
- Action: Look for the subtle AIs around you: your smart thermostat learning your schedule, your vacuum robot mapping your house, or your phone’s autocorrect suggesting the next word. Recognizing these examples makes the abstract concept of AI concrete and relatable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Thinking About AI
To truly grasp AI, you need to shed some common misconceptions:
- Mistake: Believing today’s AI is “conscious.”
- Reality: All current, working AI is Narrow AI. It is a tool, not a sentient being. It simulates intelligence; it doesn’t possess it.
- Mistake: Assuming AI is a single program.
- Reality: AI is a broad field of study encompassing many distinct technologies, like ML, Deep Learning, and Computer Vision, which are often used in combination.
- Mistake: Confusing Data Science with AI.
- Reality: Data Science is the umbrella that uses various methods to extract knowledge from data. AI uses the knowledge gained from data to make decisions or generate new content.
- Mistake: Thinking AI means “robots.”
- Reality: The majority of AI exists purely as software in the cloud (like recommendation algorithms or LLMs). Robotics is just one application of AI.
- Mistake: Assuming AI is only about the future.
- Reality: You interact with AI hundreds of times a day via your phone’s digital assistant, your bank’s fraud detection, and your email’s spam filter. It’s a technology of the present.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is best defined as the science of making machines intelligent, enabling them to mimic human cognitive functions like learning, problem solving, and perception.
It is not one thing, but a powerful ecosystem: AI is the goal, Machine Learning is the method, and Deep Learning is the advanced technique used to build the narrow, specialized AI tools that power our modern world.
The journey from a theoretical concept to the current generative AI boom has been long and winding, driven by breakthroughs in computing power and data.
By understanding the core concepts and the difference between Narrow AI and the theoretical Strong AI, you are now equipped to navigate, utilize, and discuss the world of artificial intelligence with true expertise.





Pingback: The Ultimate 7-Step Framework to Master AI Training and 10x Your Career
Pingback: AI Deep Learning: The Ultimate Guide for Beginners & Experts
Pingback: Large Language Model (LLM) Explained: Architecture, Apps, and Future
Pingback: What is Machine Learning? Types, Pipeline, and Examples
Pingback: Best AI Code Assistants in 2025: Reviews & Comparison Guide